Understanding Colorectal Cancer: Current Evidence, Early Detection, and Advances in Endoscopy
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer globally, with projections estimating 3.2 million new cases by 2040 (Morgan et al., 2023). While CRC affects individuals across all age groups, including those without clear risk factors, evidence supports the role of modifiable factors such as reducing alcohol use and smoking, dietary considerations, and increasing physical activity as part of a comprehensive risk-reduction strategy (Roshandel et al., 2024).
Detection and removal of precancerous colorectal lesions remains a cornerstone of CRC control (Roshandel et al., 2024). Advances in endoscopy continue to strengthen early identification and diagnostic accuracy (Li et al., 2024). Endoscopic evaluation contributes to diagnosis, prognosis prediction, treatment planning, and quality improvement efforts, while emerging technologies and artificial intelligence show promise for improving precision and procedural outcomes (Li et al., 2024; Kuellmer et al., 2019; Kuntz et al., 2021; Ohata et al., 2022).
Despite CRC’s global prevalence and rising incidence in younger adults, progress in endoscopic innovation, early detection, and collaborative clinical practice has significantly enhanced the identification and removal of precancerous lesions (Deshmukh et al., 2022; Morgan et al., 2023). Ongoing advancements and cross-disciplinary collaboration remain essential for strengthening CRC management (Li et al., 2024).
Learn more about CRC including endoscopic techniques, risk factors, and preventions by reviewing the references cited in this post.
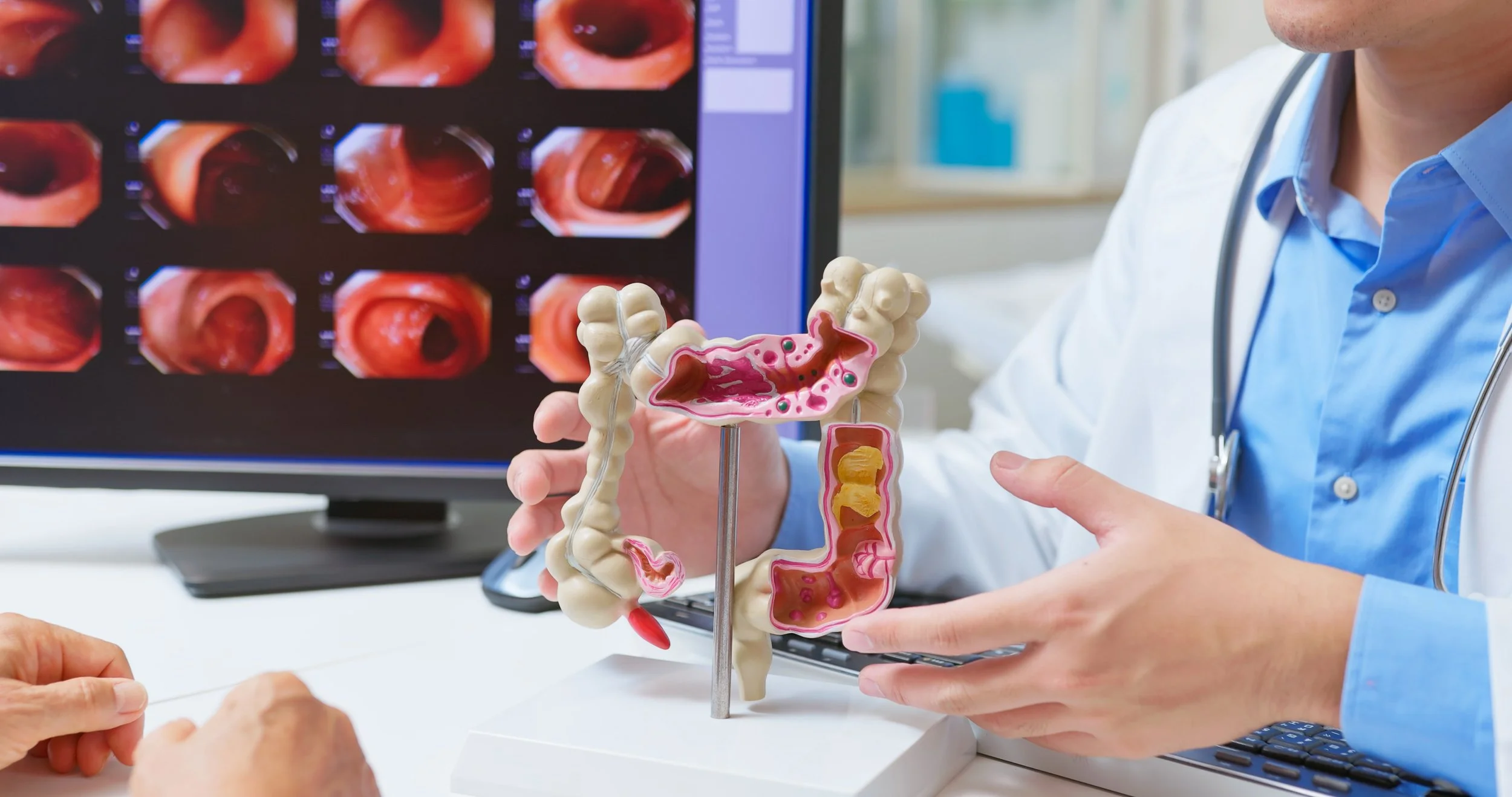
A physician explaining colon cancer to a patient.