TIMS Resources
Blog
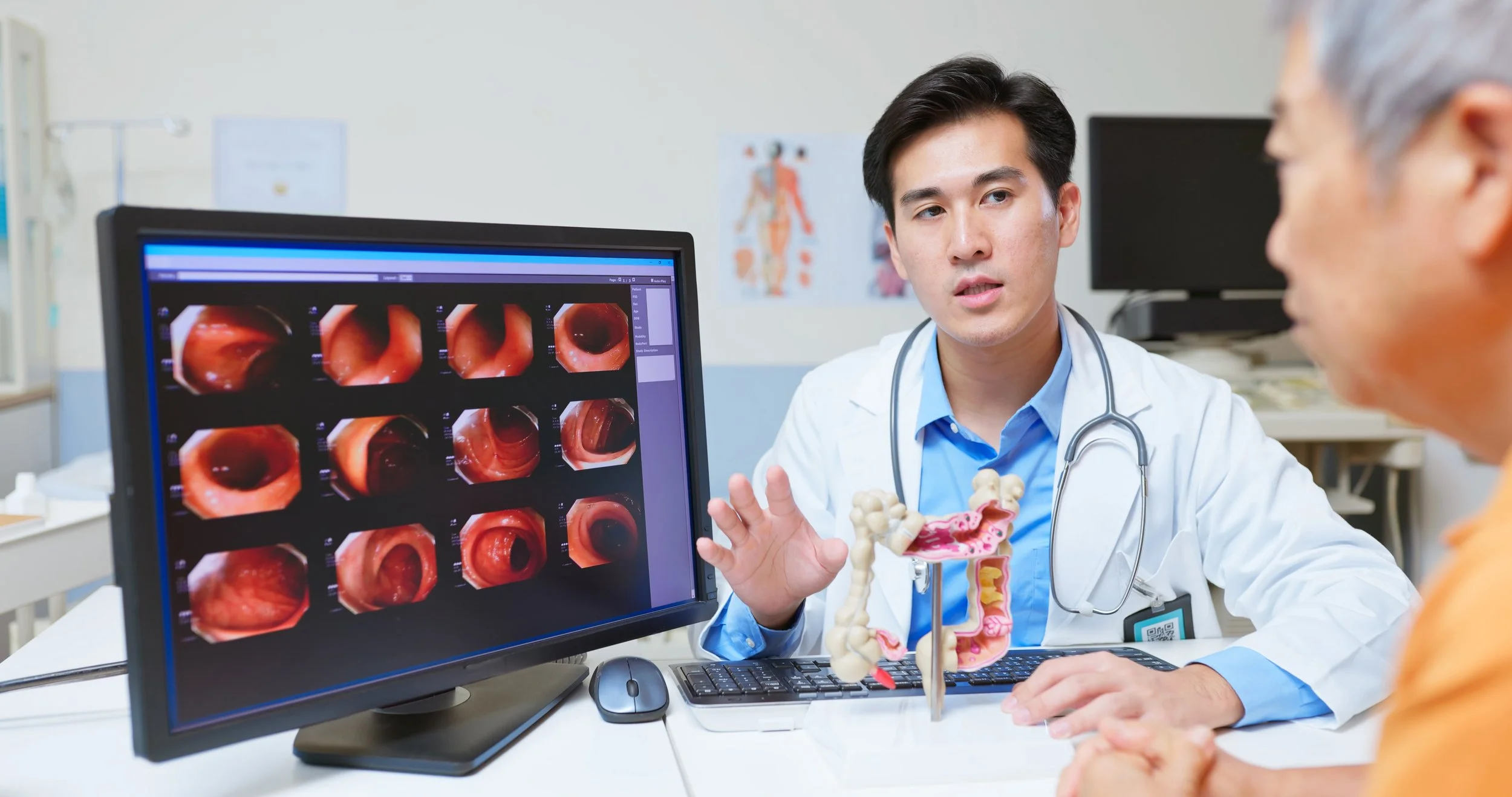
Understanding Colorectal Cancer: Current Evidence, Early Detection, and Advances in Endoscopy
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer globally, impacting individuals across all age groups. Evidence supports the role of modifiable factors such as reducing alcohol use and smoking, dietary considerations, and increasing physical activity as part of a comprehensive risk-reduction strategy.
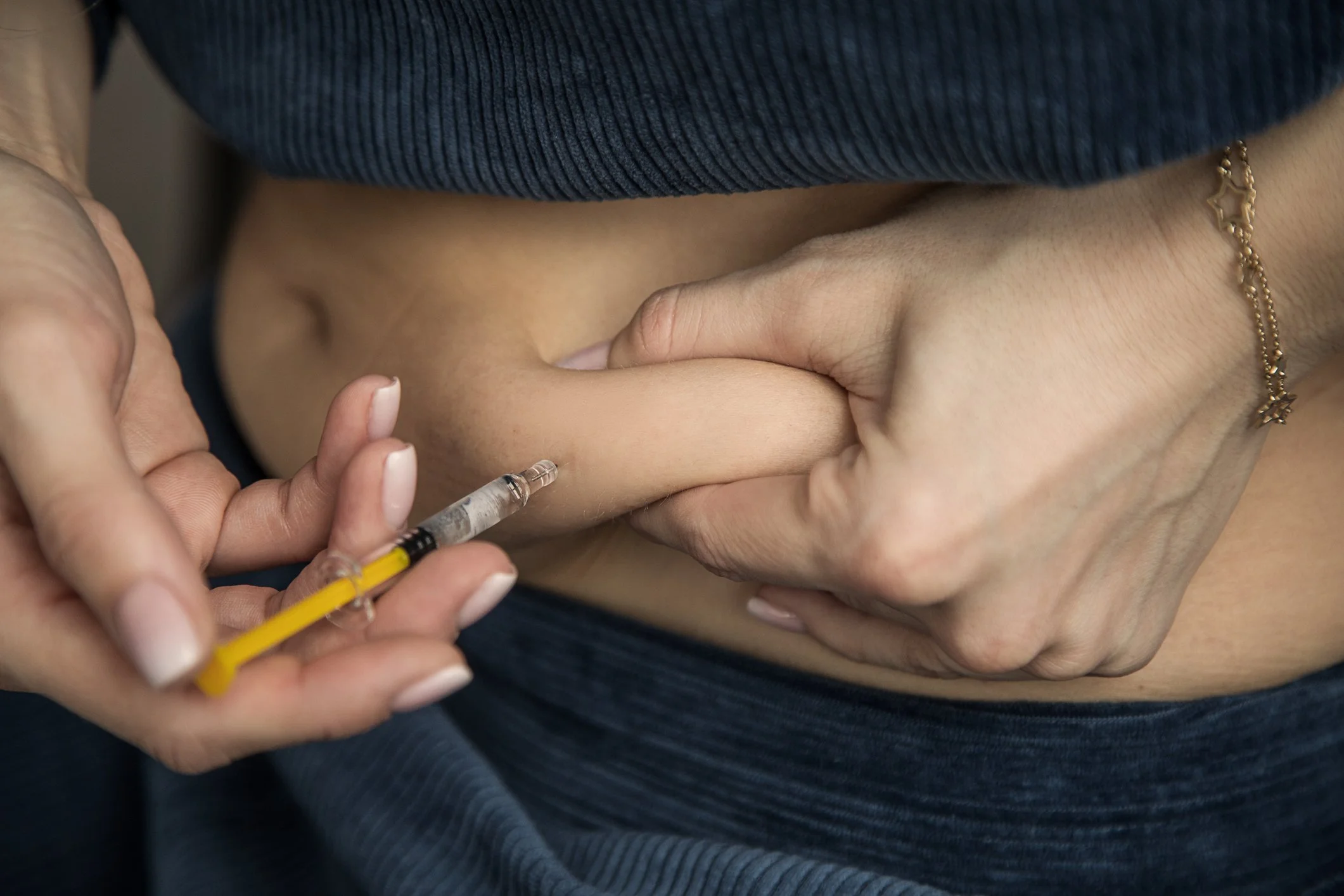
Semaglutide and the Aerodigestive System: Emerging Evidence and Monitoring Strategies
Semaglutide use has increased rapidly in recent years, and while it offers important benefits, growing research highlights potential gastrointestinal considerations.

Understanding Dysphagia in Huntington’s Disease: Prevalence, Risks, and Clinical Considerations
Huntington’s disease is a rare neurodegenerative disease which impacts movement, cognition, and swallow function, among other issues. Learn how dysphagia develops in HD, why early instrumental evaluation is essential, and what clinicians can do to improve patient outcomes.

Understanding Dysphagia in Myasthenia Gravis: Implications and Management Strategies
Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by fatigable muscle weakness, which can result in manifestations including dysarthria, dysphagia, and respiratory issues. Imaging is critical in diagnosing the presence and severity of dysphagia secondary to MG, and in determining underlying impairments.

Color and Consistency Matter: How Puree Type and Dye Impact FEES
Recent research shows that even small changes in the type or color of pureed foods and liquids can significantly impact FEES analysis. Findings highlight the importance of standardizing bolus presentations to ensure accurate assessment and informed clinical decision-making.

Sjögren Syndrome and Swallowing: Navigating Multisystem Impacts
Sjögren Syndrome is a complex autoimmune disorder most commonly recognized for causing dry eyes and dry mouth, however, its impact extends far beyond these hallmark symptoms, often affecting multiple organ systems including the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, kidneys, and nervous system.

Supporting Quantitative Data with TIMS
The field of speech-language pathology has evolved significantly, shifting from subjective impressions to objective, evidence-based assessments. TIMS MVP support advancements in the field through features such as label sets, study review, quantitative data collection, and standardized analysis. Learn how Jo Puntil, MS, CCC-SLP, BCS-S implement TIMS in their practice.

Feeding Tubes and Supporting Oral Intake for those with Dementia
Dementia involves a gradual and persistent decline in cognitive function, which impacts millions of people today. As dementia progresses, swallowing issues are likely to develop. Individuals living with dementia and caregivers may be faced with the need to consider options to support nutrition and hydration.
Optimizing Outcomes Following Lung Transplant with Dysphagia Evaluations
Pulmonary transplant is considered a gold-standard treatment for individuals experiencing end-stage lung disease. Current literature demonstrates that individuals undergoing lung transplants experience an increased risk for the development of dysphagia as well as morbidity.

Endoscopic Leak Testing, Equipment Longevity, and Patient Safety
Endoscopic reprocessing is critical for patient safety and equipment longevity. A lack of leak testing or improper leak testing can lead to scope damage and infection control issues.

Managing Dysphagia in Parkinson's Disease: Early Detection, Assessment, and Interdisciplinary Care
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that results in both motor and non-motor dysfunction with hypothesized multifactorial causes.
PD can result in a variety of symptoms including bradykinesia, resting tremor, rigidity, loss of smell, sleep dysfunction, excess saliva, constipation, mood disorders, dysphagia, excessive limb movements in sleep and others.

Dysphagia Following Extubation
Dysphagia following extubation is a commonly occurring issue for critically ill adult patients,and is correlated with increased health care costs, prolonged enteral feeding, increased risk for the development of pneumonia, and a predictor of all-cause mortality.

Barrett’s Esophagus: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
Barrett’s esophagus, a precancerous condition, is typically acquired and often caused due to chronic gastroesophageal reflux (GERD). In addition to GERD, risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus include past or current smoking history, age >50 years, family history or Barrett’s of esophageal adenocarcinoma, genetic mutations, obesity, male genotype, among others.

Navigating Eosinophilic Esophagitis: From Symptoms to Solutions
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic immune or antigen-mediated process - initiated or influenced by the presence and interaction of antigens with the immune system. EoE causes inflammation of the esophagus and a buildup of eosinophils.
Previously, EoE was thought to be a component of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), however, it is now understood to be a separate issue.

St. Louis Children’s Hospital Adopts TIMS Connect to Expand Access to Pediatric Fluoroscopy
We are honored to support St. Louis Children’s Hospital, a Division of BJC HealthCare, in their efforts to enhance pediatric imaging services through the adoption of TIMS Connect. By leveraging this innovative solution, St. Louis Children’s is improving access to fluoroscopic procedures while continuing to deliver the highest standard of care in a patient-centered environment.

Foundational Information - Pediatric Dysphagia and Feeding Disorders
Research demonstrates the prevalence of pediatric feeding disorders (PFD) and pediatric dysphagia. Both PFD and dysphagia can result in significant ramifications, such as aspiration, adverse pulmonary issues secondary to oral intake, limited intake of quality or variety of foods/liquids, disruptive behaviors during mealtimes, challenges using utensils, nutrition and hydration concerns, difficulty with growth and/or weight, among other issues (ASHA, n.d.; Goday et al., 2019; Arvedson et al., 2019).

Enhancing Dysphagia Education: Maryville University Utilizes TIMS MVP and TIMS Review
We are honored to highlight Maryville University's commitment to advancing dysphagia education through the integration of TIMS MVP and TIMS Review into their graduate school curriculum. This semester, students have had invaluable hands-on experience with the use of TIMS MVP and TIMS Review to enrich their understanding and practical skills in dysphagia assessment and treatment.

The Revised Patterson
Internal lymphedema is prevalent for people with head and neck cancer. Jeans et al. (2023) report that more than 96% of people with head and neck cancer develop internal lymphedema, resulting in dysphagia as well as the occurrence of penetration and aspiration. The Revised Patterson Edema Scale represents a valuable advancement in the assessment of laryngeal and pharyngeal edema following treatment for head and neck cancer.

Colorectal Cancer: Prevalence, Risk Factors and Prevention
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second most common cause of cancer death in the United States. CRC is rapidly shifting to diagnosis at a younger age, at a more advanced stage, and in the left colon/rectum. Many colon cancer cases are sporadic, with approximately 5 percent attributed to inherited genetic mutations and familial adenomatous polyposis.

An Overview About Retrograde Cricopharyngeal Dysfunction (RCPD)
Retrograde Cricopharyngeal Dysfunction (RCPD) is characterized by the inability to burp as well as associated symptoms including loud gurgling noises, chest and abdominal pain, and excessive flatulence. It is hypothesized that RCPD is caused by inability of the cricopharyngeal sphincter to relax during esophageal distention.

